Research
Position Synchronization Control for Networked Multi-axis Servo Systems
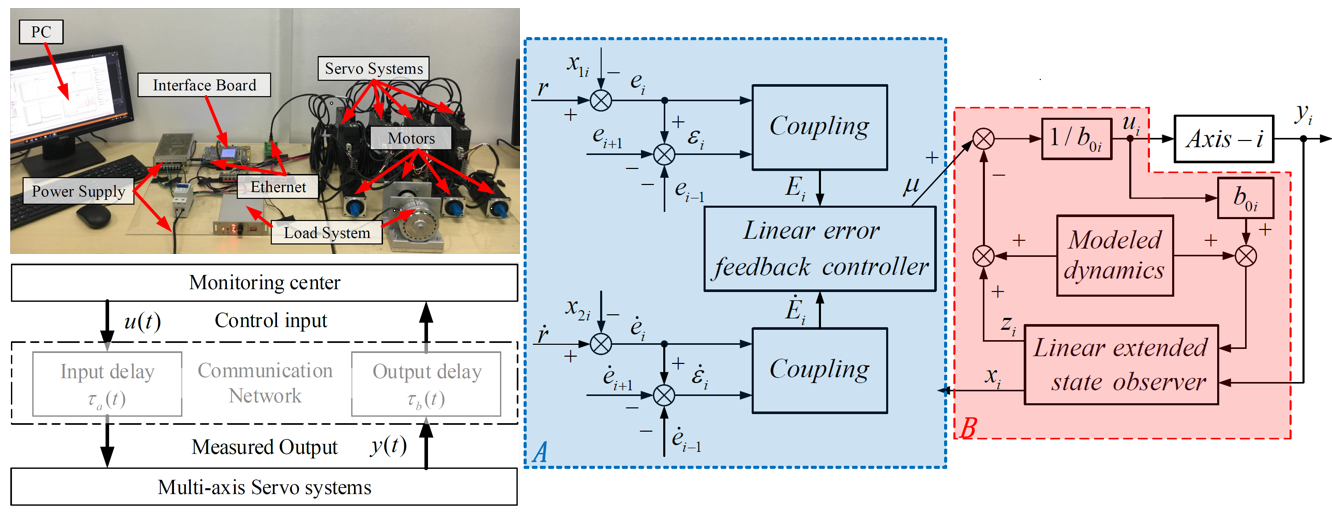 |
Position synchronization control (PSC) for multi-axis servo systems is a crucial part in manufacturing industry, which is used to ensure that all machine shafts move synchronously and coordinately according to a certain proportion during the motion. With the rapid development of network communication technologies, both academia and industry have attempted to implement the PSC for networked motion control systems (NMCSs), for example, the computer numerical control (CNC) systems, the surface mount systems, the electric multiple units, and the robotic arms. Although the application of the NMCS brings many benefits, such as simplified wiring, powerful extensibility and easy maintenance, it also raises several new challenging issues. One of them is the network-induced delay, which may seriously degrade system performances. An effective method to address this problem is to consider the time delay as a network disturbance and compensate for it using approaches based on disturbance observers.
Qi Wu, Shijian Dong, Wen-An Zhang† and Li Yu. Online modeling of the CNC engraving system with dead-zone input nonlinearity. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(1): 774-782, doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.3044819.
Qi Wu, Li Yu, Yao-Wei Wang and Wen-An Zhang†. LESO-based position synchronization control for networked multi-axis servo systems with time-varying delay. IEEE-CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2020, 7(4): 1116-1123, doi: 10.1109/JAS.2020.1003264.
Intelligent Fault Diagnosis for Mechanical Equipments based on Monitoring Signals
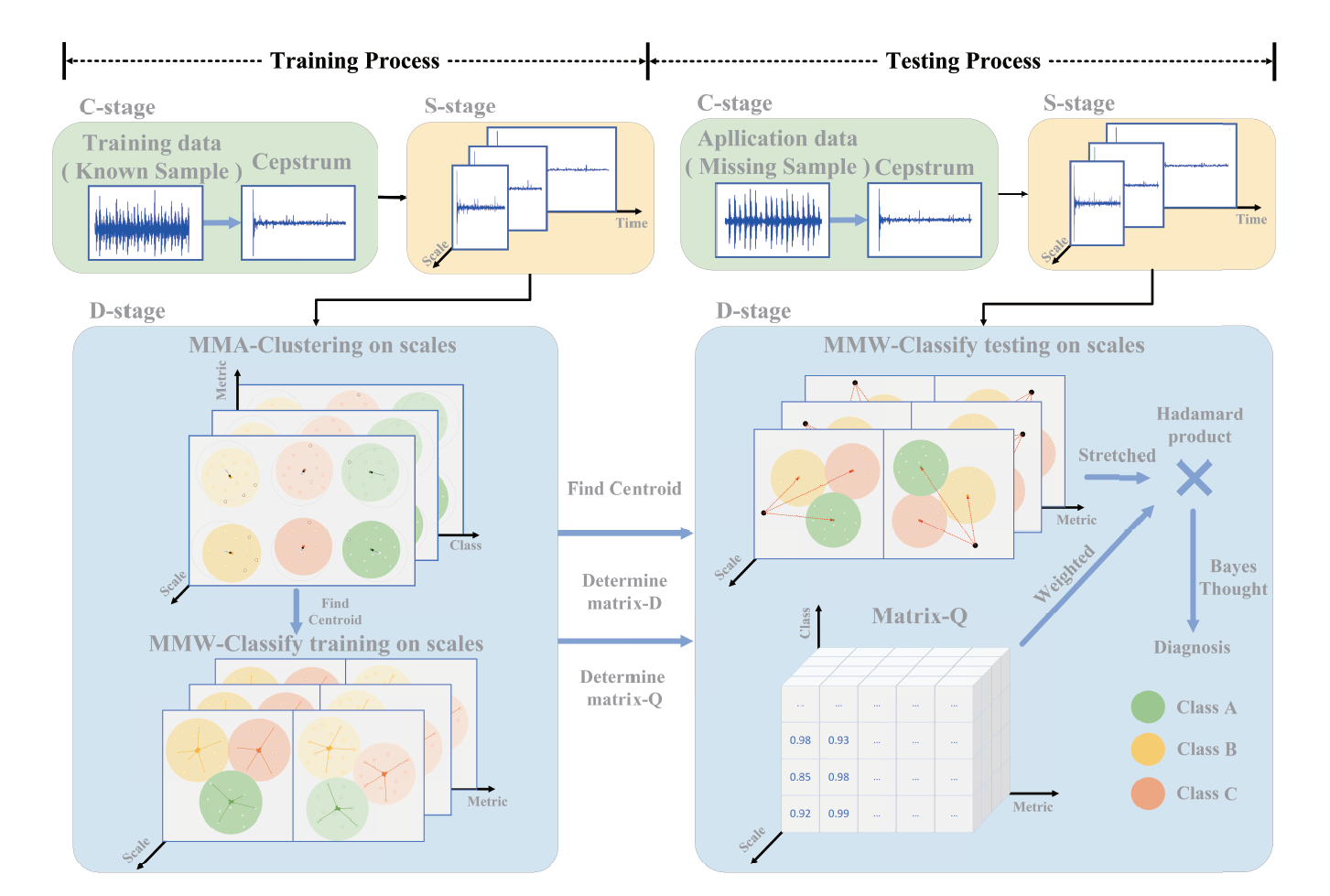 |
Fault diagnosis is an approach designed to comprehend and assess the operational state of mechanical equipment, determining its overall or partial normalcy or abnormality which is employed in the health management of sizable machinery, including wind turbines, ship motors, gas turbines, aviation engines, and cranes. Nevertheless, the progression of intelligent manufacturing has resulted in an escalation of structural complexity and precision in mechanical equipment, introducing challenges such as nonlinearity, non-stationarity, incompleteness, incomplete information, and insufficient fault category coverage in operational monitoring data. Consequently, time and frequency domain feature extraction methods based on wavelet packet decomposition and analysis of cepstrum are used to extract features characterizing prominent faults. Simultaneously, multi-scale analysis methods are applied to capture additional fault-related information, thereby enhancing the accuracy of fault diagnosis.
Dajian Huang, Wen-An Zhang† and Steven X. Ding. Bearing fault diagnosis with incomplete training data: Fault data with partial diameters. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, Early access. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2023.3294811.
Dajian Huang, Wen-An Zhang†, Fanghong Guo, Weijiang Liu and Xiaoming Shi. Wavelet packet decomposition-based multiscale CNN for fault diagnosis of wind turbine gearbox. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(1): 443-453. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3123667.
Dajian Huang, Xiufang Shi and Wenan-An Zhang†. False data injection attack detection for industrial control systems based on both time- and frequency-domain analysis of sensor data. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(1): 585-595. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3007155.
Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning
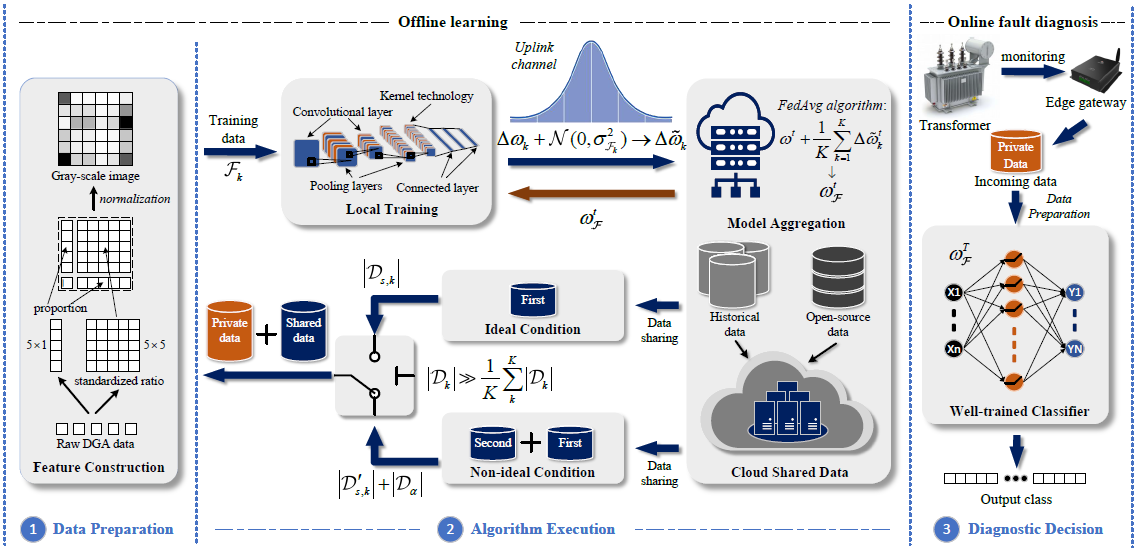 |
Power transformer (PT) is one type of transformer used for electrical energy transmission. The health of the PT plays an essential role in the reliability and supply sustainability of electricity. Recently, there have been numerous literatures devoted to improving the maintenance and repair capability of PTs from the perspective of the prognostics health management. Among them, unbalanced learning and data security in power transformer fault diagnosis are still open issues. The emergence of federated learning (FL) has provided a secure and distributed learning framework. But, there are still two issues that need to be addressed before using the FL-based fault diagnosis methods. The first issue is the statistical challenge brought by the variability of unbalanced data in data quantity and category distribution. The second issue is the trade-off between model performance and the level of privacy protection. To address such challenges, we have designed data-sharing and privacy-preserving strategies, that is alleviating the impact of imbalanced data on model training by sharing global data and safeguarding private data by injecting Gaussian noise into the uploaded parameters.
Qi Wu, Chen Dong, Fanghong Guo†, Lei Wang, Xiang Wu and Changyun Wen, Privacy-preserving federated learning for power transformer fault diagnosis with unbalanced data. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, Early access.
Fault-tolerant Control for Multi-agent Systems
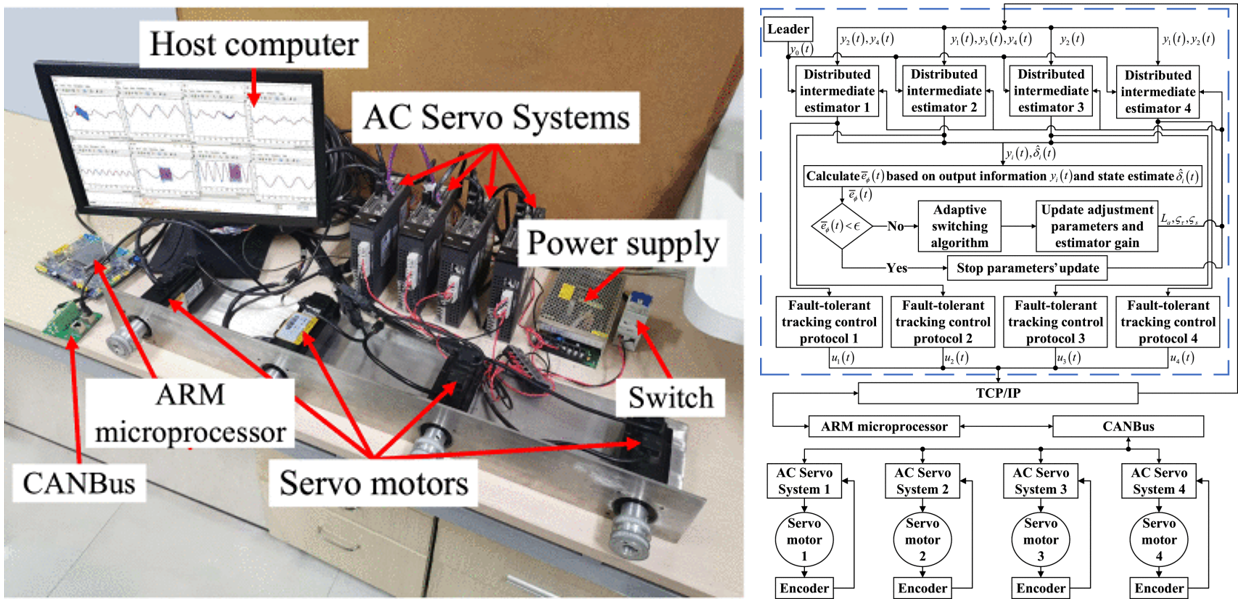 |
Multi-agent systems (MAS) have received increasing attention due to their wide range of applications in areas such as collaboration, formation flying, and vehicle networking. However, the probability of failure has increased greatly due to the expansion of the system scale. The failure of any node may spread its effect to the whole system through the communication network. Therefore, the problem of fault-tolerant control of MAS has increasingly become a research focus. Existing observer-based frameworks have some limitations: 1) Most of the existing observers are designed offline, i.e., the parameters are chosen in advance, which lacks flexibility.2) There is no explicit optimization scheme for online fault estimation. To address these challenges, a new structured distributed intermediate estimator is proposed. In addition, a reinforcement learning estimation strategy is introduced to achieve online dynamic tuning of key parameters, thus improving the real-time estimation performance.
Caoyuan Gu, Junwei Zhu†, Wen-An Zhang, Li Yu and Hui Dong. Intrusion-tolerant synchronous control for networked multi-axis motion control system, Control and Decision, 2019, 34(11): 2289-2296, doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2019.0537. (in Chinese)
Junwei Zhu†, Caoyuan Gu, Steven X. Ding, Wen-An Zhang, Xin Wang and Li Yu. A new observer-based cooperative fault-tolerant tracking control method with application to networked multiaxis motion control system. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 68(8): 7422-7432, doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.3001857.
Junwei Zhu†, Caoyuan Gu, Ding Wang, Wen-An Zhang and Xin Wang. Design of an intelligent cooperative fault-tolerant trajectory tracking control system for multi-servo motors. Control Theory & Applications, 2021, 38(7): 1023-1032, doi: 10.7641/CTA.2021.00627. (in Chinese)